Secure your SSH Logins on Linux - Steps to Enable Passwordless Login
Enable Passwordless SSH Logins on Linux
This method of authentication is more secure than using a password because it is less susceptible to brute-force attacks and other forms of password cracking. Additionally, it allows for automated connections between systems, which is useful for tasks such as backups and automation scripts. By enabling passwordless SSH logins, you can simplify and streamline your workflow, while also improving the security of your system.
To enable
passwordless SSH logins on Linux, you need to follow these steps:
1. Generate SSH Key
Pair:
· Open the terminal on your Linux system.
· Type the following command to generate an SSH key pair:
· Press the Enter key to accept the default options for the key pair.
· This command will generate two files in the ~/.ssh directory: id_rsa
(private key) and id_rsa.pub (public key).
2. Copy Public Key to
the Remote Server:
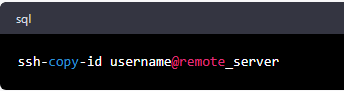
· Type the following command to copy the public key to the remote server:
· Replace "username" with your username and
"remote_server" with the IP address or hostname of the remote server.
· Enter your password when prompted.
· This command will add the public key to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file
on the remote server.
3. Test the
Connection:
· Type the following command to connect to the remote server:
· Replace "username" with your username and
"remote_server" with the IP address or hostname of the remote server.
· You should now be able to connect to the remote server without entering
a password.
4. Optional: Disable
Password Authentication:
· Open the SSH configuration file on the remote server:
· Find the line that says "PasswordAuthentication" and change
its value to "no".
· Save and close the file.
· Restart the SSH service
· From now on, you will only be able to connect to the remote server using
your SSH key pair, and password authentication will be disabled.
That's it! You have
now enabled passwordless SSH logins on your Linux system.






Post a Comment